Ultimate Guide to Dive Watches (Purpose and Features Explained)
Dive watches aren't just fancy timepieces that look good with a wetsuit. These specialized instruments serve a critical purpose of dive watches - keeping divers safe underwater by accurately tracking time and depth limits. When you're 100 feet below the surface, knowing exactly how long you've been down can mean the difference between a safe ascent and a dangerous situation.
The world of dive watch features goes far beyond basic timekeeping. These robust companions pack serious engineering into their cases, from pressure-resistant construction to luminous displays that glow in the darkest depths. Whether you're a professional diver, weekend snorkeler, or someone who appreciates bulletproof craftsmanship, understanding what makes these watches tick helps you appreciate why they've become icons both underwater and on dry land.
A Brief History of Dive Watch Development
Dive watches emerged in the 1950s when recreational scuba diving exploded in popularity and military diving operations demanded reliable underwater timekeeping. The ocean called for instruments that could handle crushing pressure, corrosive saltwater, and complete darkness while maintaining split-second accuracy.
The Blancpain Fifty Fathoms launched in 1953 as one of the first purpose-built dive watches, featuring 91-meter water resistance and a rotating bezel for timing dives. Rolex followed with the Submariner in 1953, establishing design principles that still define modern dive watches today.
The 1960s brought an innovation arms race as watch companies competed to create more capable dive instruments. Water resistance ratings climbed from 100 meters to 200, then 300 meters and beyond. Automatic movements became standard, eliminating manual winding that could compromise water seals during critical underwater moments.
Professional diving in the 1970s and 1980s pushed dive watch features into extreme territory. Helium escape valves appeared to handle saturation diving, where commercial divers lived in pressurized chambers for days. Case sizes grew to accommodate larger movements and improved readability, establishing the robust aesthetic that defines modern dive watches.
Today's dive watches represent decades of refinement, combining traditional mechanical reliability with advanced materials like ceramic bezels and titanium cases. The fundamental purpose of dive watches remains unchanged - providing fail-safe timing and uncompromising reliability when lives depend on accurate timekeeping.
What is a Dive Watch?
A dive watch is a specialized timepiece engineered to meet strict international standards for underwater use, going far beyond basic water resistance to provide life-saving functionality for divers. These instruments must survive crushing water pressure, temperature extremes, and physical impacts while maintaining precise timekeeping in conditions that would destroy regular watches.
The ISO 6425 standard, established in 1996, defines what qualifies as a true dive watch versus a simple water-resistant timepiece. To earn dive watch status, a watch must handle water pressure equivalent to at least 100 meters depth while maintaining accurate timekeeping throughout the test.
Real dive watches undergo rigorous testing that simulates actual diving conditions. Manufacturers subject these timepieces to pressure chambers replicating crushing depths, temperature fluctuations mimicking changing water conditions, and shock tests representing real-world impacts from rocks or equipment.
The purpose of dive watches extends beyond basic timekeeping to include critical safety functions. These instruments help divers track elapsed bottom time, monitor decompression limits, and maintain awareness of their dive profile. In emergency situations, accurate timing can mean the difference between safe ascent and potentially fatal decompression sickness.
True dive watches also feature anti-magnetic properties to resist interference from diving equipment, shock resistance to handle underwater impacts, and luminous displays readable in complete darkness. These requirements separate genuine dive instruments from fashion watches that simply look sporty.
What are the Features of a Dive Watch?
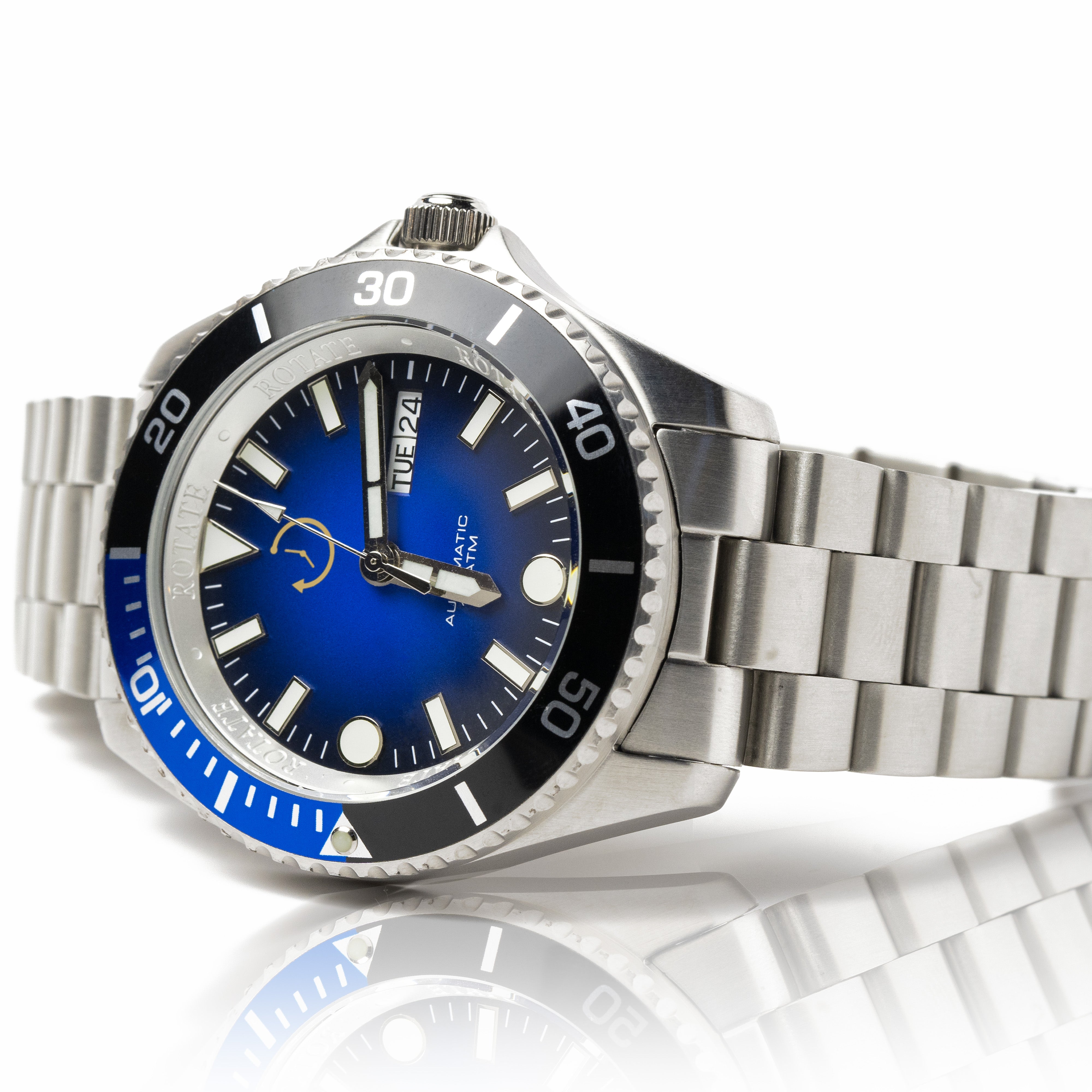
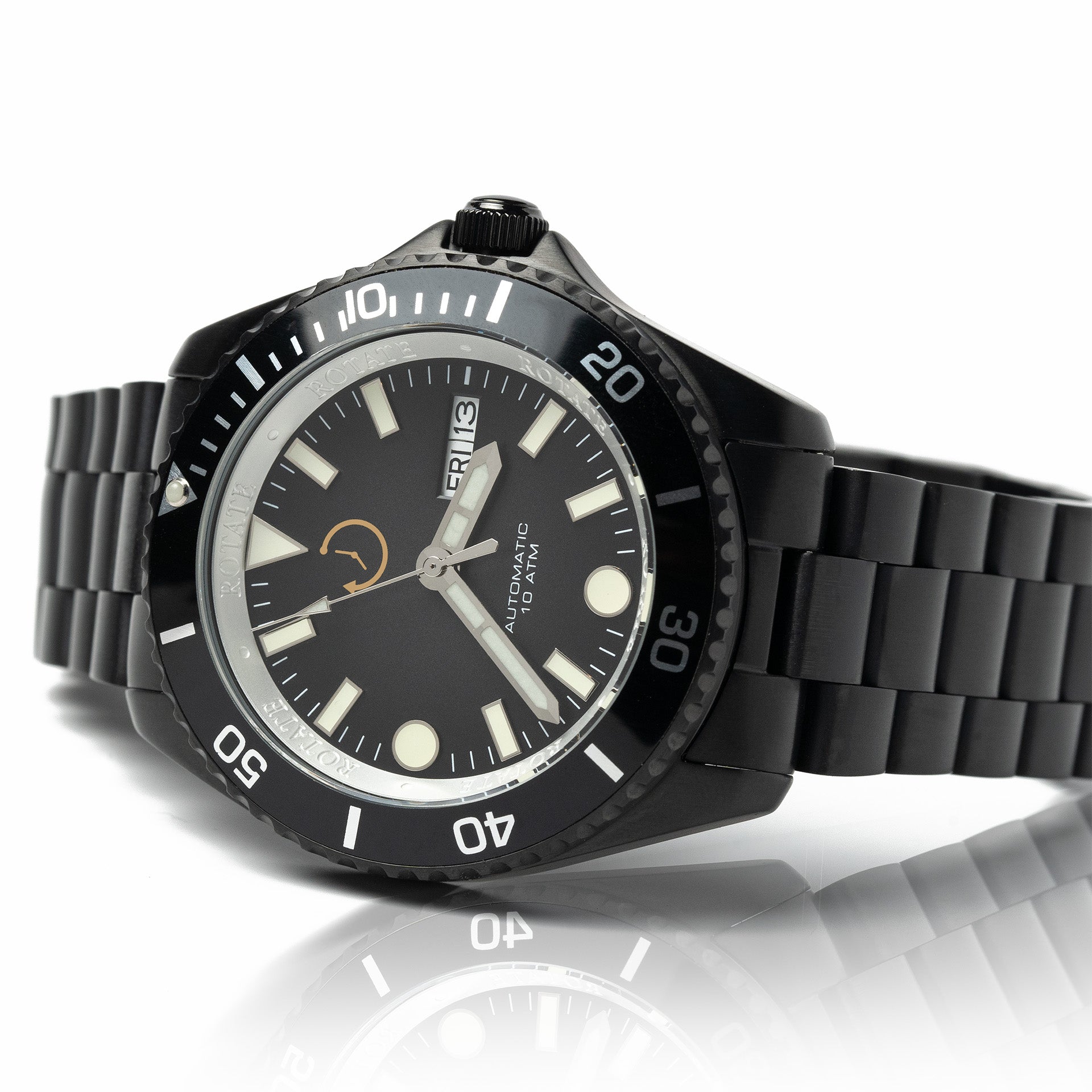
1. Water Resistance That Saves Lives
Dive watch features start with bulletproof water resistance that goes far beyond marketing numbers. Most quality dive watches offer 300-meter protection, providing substantial safety margins for recreational diving while maintaining reasonable case thickness. The engineering involves screw-down crowns creating watertight seals and case backs that lock moisture out completely.
Professional diving watches push these limits to 1,000 meters or beyond, incorporating helium escape valves that prevent case damage during commercial diving operations. These valves automatically release built-up gases during decompression, protecting the crystal from explosive pressure changes that could shatter regular watches.
2. Rotating Timing Bezels for Safety
The rotating bezel ranks among the most critical dive watch features for underwater safety. This tool allows divers to mark descent time by aligning the bezel's arrow with the minute hand at dive start. As time passes, the gap between arrow and minute hand shows elapsed dive time instantly.
Most dive watch bezels rotate only counterclockwise, preventing accidental adjustments that could show less elapsed time than actual. This safety feature ensures divers never accidentally extend bottom time beyond safe limits. The bezel's first 15-20 minutes feature detailed markings since these represent the most critical timing periods for recreational diving.
3. Luminous Displays for Dark Water Visibility
Sunlight disappears quickly underwater, making luminous displays essential for reading dive watches in low-light conditions. Modern dive watches use Super-LumiNova or similar phosphorescent materials that charge from ambient light and glow for hours in complete darkness.
The hands, hour markers, and bezel triangle all receive luminous treatment for maximum visibility. Large, clearly defined markers and thick hands ensure divers can quickly check their watch without squinting or adjusting position. Many dive watches use contrasting colors like green luminous material against blue dials to enhance underwater readability.
4. Toughened Construction Materials
Dive watches face environments that would destroy regular timepieces within hours. Salt water corrodes metal components, pressure changes stress cases and crystals, and physical impacts from rocks or equipment test every connection point.
Stainless steel cases provide the foundation for most dive watches, offering excellent corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratios. Titanium appears in premium models, delivering superior lightness and biocompatibility for extended wear. Sapphire crystals rank just below diamond in hardness, resisting scratching from sand, rocks, or diving equipment.
5. Automatic Movements for Reliability
Quality dive watches typically feature automatic movements that wind themselves through natural wrist motion. This eliminates the need for manual winding that could compromise water seals during diving operations. Modern automatic movements include shock protection and robust construction specifically designed for active underwater use.
The self-winding mechanism actually benefits from diving activity, as arm movements keep the mainspring wound throughout extended diving sessions. Many automatic dive watch movements provide 40+ hour power reserves, ensuring continued operation through multi-day diving trips.
Top 10 Best Dive Watches Available Today
1. Rolex Submariner
The Submariner defined dive watch aesthetics for generations and continues setting industry standards today. Its 300-meter water resistance, Cerachrom ceramic bezel, and legendary Perpetual movement deliver Swiss chronometer accuracy within -2/+2 seconds per day. The 3135 caliber movement provides a 48-hour power reserve and has proven itself through decades of professional diving use.
The unidirectional rotating bezel features a Cerachrom insert that's virtually scratchproof and fade-resistant. Chromalight luminous display glows blue in darkness and lasts twice as long as traditional luminous materials. Current models measure 40mm in diameter with 300-meter depth rating, making them suitable for all recreational diving activities.
2. Rolex Deepsea Challenge 'James Cameron'
Built for extreme depth exploration, this titanium giant handles an incredible 11,000-meter water resistance - deeper than any ocean trench on Earth. The experimental case construction uses a 5.5mm thick sapphire crystal and titanium case back to withstand crushing pressures that would implode regular watches.
The specially modified 3135 movement maintains chronometer accuracy even under extreme pressure. The watch weighs significantly less than steel despite its massive 50.2mm case diameter, thanks to grade 5 titanium construction. This represents the absolute pinnacle of dive watch engineering, though its size limits practical daily wear.
3. Blancpain Fifty Fathoms
The watch that started the modern dive watch category still impresses with its clean dial layout and 300-meter water resistance. The automatic 1315 caliber movement features a 120-hour power reserve and silicon balance spring for enhanced magnetic resistance and accuracy of +6/-4 seconds per day.
The 45mm case accommodates larger hour markers for improved underwater readability, while the unidirectional rotating bezel uses traditional markings that inspired countless imitators. The moisture indicator at 6 o'clock changes color if water enters the case, providing an early warning system for seal failure.
4. Omega Seamaster 300
Omega's professional dive watch combines proven reliability with cutting-edge technology. The helium escape valve handles commercial diving requirements while the Co-Axial Master Chronometer movement maintains exceptional accuracy of 0/+5 seconds per day and resists magnetic fields up to 15,000 gausses.
The 42mm case offers 300-meter water resistance with a unidirectional rotating bezel featuring a ceramic insert. The wave-pattern dial and sword hands provide excellent readability underwater, while the automatic movement delivers 60-hour power reserve for extended diving expeditions.
5. Doxa SUB 300T
This cult classic brought bright orange dials to dive watches, creating instant underwater visibility that influenced countless designs. The distinctive cushion case shape and patented no-decompression limit timing bezel layout remain unique in the diving world.
The Swiss ETA 2824-2 movement provides reliable automatic timekeeping with 38-hour power reserve and accuracy within COSC chronometer standards. The 42.5mm steel case offers 300-meter water resistance, while the signature orange dial maintains excellent contrast in varying light conditions underwater.
6. Jaeger-LeCoultre Deep Sea Alarm
One of the few dive watches with an audible alarm function, warning divers when preset time limits approach. The compression-proof case and specialized automatic movement represent Swiss high-end watchmaking applied to serious diving tools.
The 39mm case handles 300-meter depths while the alarm mechanism uses a hammer striking the case back to create sound audible underwater. The movement maintains accuracy within -20/+40 seconds per day and provides a 45-hour power reserve. Limited production makes these watches particularly sought-after among diving professionals.
7. Seiko Professional Diver's 600M "Grandfather" Tuna
Seiko's legendary "Tuna" series proves that outstanding dive watches don't require Swiss movements or premium pricing. The shrouded case design protects the crown and provides incredible shock resistance for professional diving operations.
The automatic 7S26 movement offers reliable timekeeping with 41-hour power reserve, while the 48mm titanium case handles 600-meter depths. The distinctive case shape and bright dial markings provide instant recognition underwater, making this a favorite among commercial and military divers.
8. Breitling Superocean
Modern dive watch design meets classic proportions in Breitling's Superocean series. The mesh bracelet option provides excellent comfort and quick-drying properties after diving, while the automatic movement features 42-hour power reserve.
The 42mm case offers 300-meter water resistance with a unidirectional rotating bezel featuring bold minute markings. The automatic Breitling 17 movement maintains accuracy within COSC chronometer standards of -4/+6 seconds per day, making it suitable for precision timing underwater.
9. Tudor Pelagos
Tudor's titanium dive watch combines lightweight construction with serious diving capability. The 500-meter depth rating exceeds most recreational diving requirements, while the helium escape valve handles professional diving operations.
The 42mm titanium case weighs 40% less than steel while offering superior corrosion resistance. The automatic MT5612 movement provides 70-hour power reserve and maintains chronometer accuracy of -2/+4 seconds per day. The self-adjusting bracelet automatically compensates for wetsuit compression during diving.
10. Citizen Promaster Diver
Citizen's Eco-Drive technology eliminates battery changes by converting any light source into power. The dive watch features 300-meter water resistance and ISO compliance for recreational diving use.
The 42mm steel case houses a quartz movement that maintains exceptional accuracy of ±15 seconds per month when fully charged. The light-powered system provides 6+ month power reserve in darkness, while the unidirectional rotating bezel features luminous markings for underwater timing.
Building Your Own Dive-Style Watch
For those who appreciate the engineering behind dive watches but want hands-on involvement in creation, DIY watchmaking kits offer an exciting alternative. These complete packages provide quality components and detailed instructions for building your own dive-style timepiece from scratch.
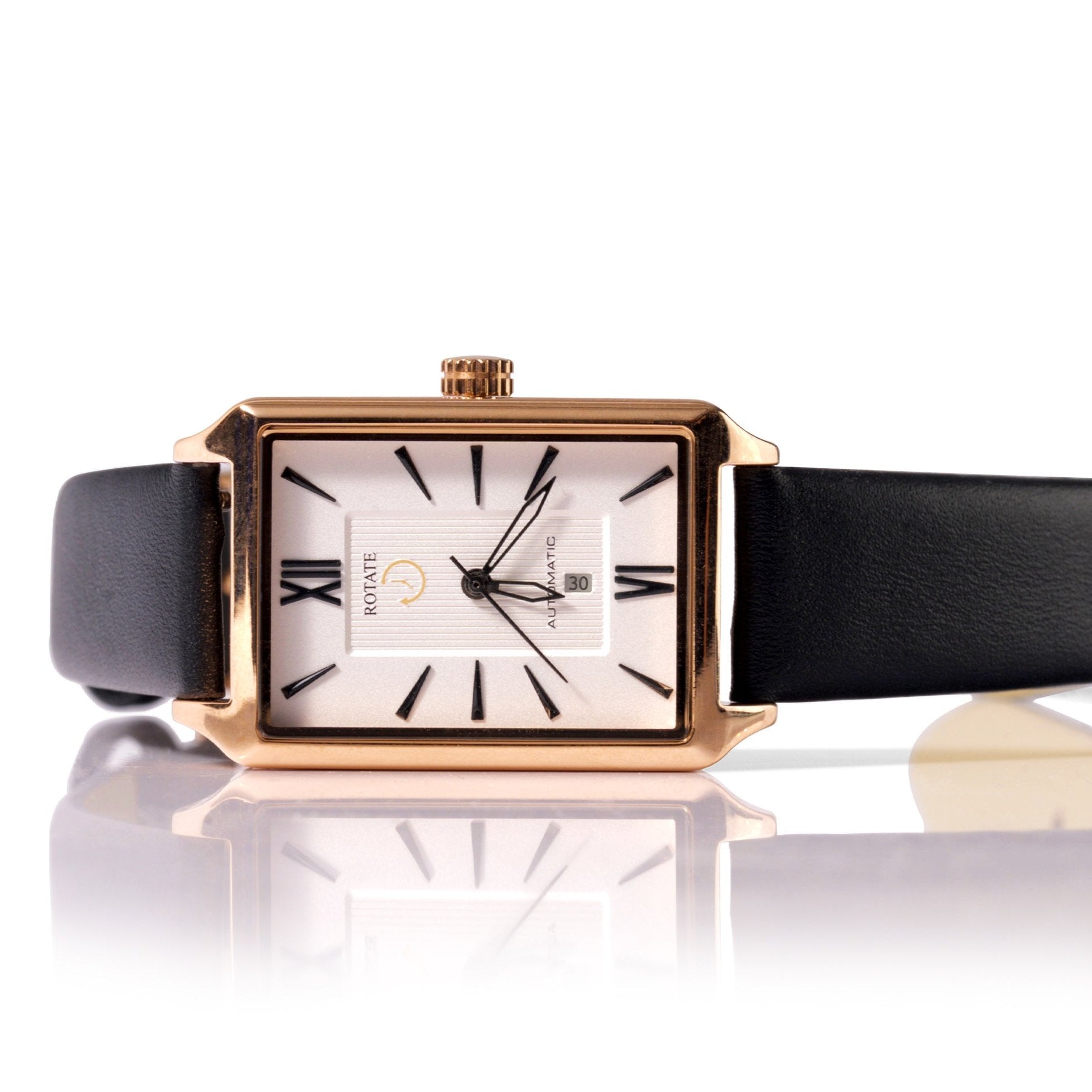
Cabot Watchmaking Kit
The Cabot DIY kit delivers everything needed to build a 43mm dive-style watch with genuine water resistance. The stainless steel case features a rotating bezel and screw-down crown, while the deep blue dial provides excellent underwater visibility.
The included Japanese Seiko NH36 automatic movement offers 41+ hour power reserve, date function, and hand-winding capability. The movement features 24 jewels and maintains accuracy comparable to Swiss movements costing significantly more.
The kit includes all necessary tools: precision screwdrivers, tweezers, spring bar tool, pliers, and protective gloves. The comprehensive assembly guide breaks down each step with detailed photos and troubleshooting tips. Assembly typically takes 2-3 hours and requires no prior watchmaking experience.
Marco Watchmaking Kit
For those preferring sleeker aesthetics, the Marco kit creates an all-black dive watch with skeleton dial elements. The same reliable Seiko NH36 movement and waterproof case construction provide dive watch capability in a more understated package.
The 43mm stainless steel case offers 10 ATM water resistance (equivalent to 100 meters), meeting ISO standards for recreational diving use. The rotating bezel features precise minute markings, while the luminous hands and markers ensure readability in low-light conditions.
Both kits feature quality components that rival watches costing hundreds more when purchased and assembled. The purpose of dive watches includes understanding how these complex machines work, making DIY assembly an educational experience that deepens appreciation for watchmaking craftsmanship.
How to Choose the Right Dive Watch for Your Needs
Step 1: Determine Your Actual Water Resistance Requirements
Most recreational divers never exceed 40 meters depth, making 200-300 meter rated dive watches perfectly adequate for normal use. Professional or technical divers requiring deeper capabilities should consider 500+ meter ratings with helium escape valves. Remember that water resistance ratings include safety margins, so a 300-meter watch handles recreational diving with room to spare.
Step 2: Decide Between Automatic and Quartz Movements
Automatic movements offer traditional mechanical appeal and unlimited lifespan with proper maintenance, while quartz provides superior accuracy and lower maintenance requirements. Dive watches with automatic movements wind themselves through diving activity and don't require battery changes during critical underwater missions. Quartz movements maintain better accuracy but need battery replacement every 2-3 years.
Step 3: Select Appropriate Case Size for Comfort and Readability
Larger cases (42-45mm) provide better underwater readability but may feel bulky on smaller wrists during extended wear. Smaller cases (38-40mm) offer superior daily comfort but sacrifice dial real estate for timing markings. Consider your wrist size and intended use - professional divers often prefer larger cases for enhanced visibility.
Step 4: Choose Quality Materials for Durability
Stainless steel cases offer excellent corrosion resistance and proven durability for most diving applications. Titanium provides superior lightness and biocompatibility but costs significantly more. Ceramic bezels resist scratching and fading better than aluminum but may crack under severe impact. Dive watch features should match your expected use intensity and environment.
Step 5: Evaluate Essential Safety Features
Unidirectional rotating bezels prevent dangerous timing errors, while luminous displays ensure readability in dark water. Screw-down crowns maintain water resistance under pressure, and shock resistance protects movement during underwater impacts. Anti-magnetic properties prevent interference from diving equipment containing strong magnets.
Step 6: Set a Realistic Budget Range
Quality dive watches exist at every price point from $200 to $20,000+. Essential features like water resistance, timing bezels, and luminous displays appear across all price ranges. Higher prices typically bring premium materials, superior movements, and enhanced finishing rather than fundamentally better diving capability. Determine which features matter most for your specific diving needs.
Key Takeaways
Dive watches serve critical safety functions beyond basic timekeeping, helping divers track elapsed bottom time and monitor decompression limits through precise timing mechanisms and fail-safe bezel systems.
Water resistance ratings include substantial safety margins, with 300-meter rated watches handling recreational diving depths up to 40 meters with significant protection against pressure variations and temperature changes.
Rotating bezels provide fail-safe timing that works regardless of battery life or electronic failures, with unidirectional rotation preventing dangerous timing errors that could extend dives beyond safe limits.
Quality materials make the difference between watches that last decades and those that fail after minimal saltwater exposure, with stainless steel, titanium, and ceramic providing proven durability for underwater use.
Automatic movements offer reliability advantages for serious diving applications, eliminating battery dependence while winding themselves through natural diving motion and providing consistent timekeeping throughout extended expeditions.
DIY watchmaking kits provide educational value while creating functional dive-style timepieces, teaching appreciation for the engineering complexity behind these life-saving instruments while delivering quality results at accessible prices.
Time isn't just measured, it's built with your own hands.
Start your watchmaking journey with Rotate Watches, where complete DIY watch kits transform curiosity into craftsmanship.
Browse our collection to find your perfect match, from complete watchmaking kits to intricate watch movement kits.
Your watchmaking story begins with a single screw. Start building today.
FAQ
Q. What makes a watch suitable for actual diving versus just swimming?
True dive watches must meet ISO 6425 standards, including water resistance of at least 100 meters, luminous displays readable in darkness, rotating timing bezels, and anti-magnetic properties. Swimming watches often lack these critical safety features and may not handle the pressure changes or saltwater exposure that diving involves. The testing standards for dive watches also include shock resistance and temperature variation requirements that swimming watches don't face.
Q. How deep can most dive watches actually go compared to their rated depth?
Dive watch depth ratings include significant safety margins, often 2-3 times the actual tested depth. A 300-meter rated watch typically handles depths around 750-900 meters in laboratory conditions. However, real-world factors like temperature changes, age of seals, and impact damage can reduce this capacity. Most recreational diving occurs between 10-40 meters, making even 200-meter rated watches extremely capable for normal use.
Q. Why do dive watches have rotating bezels instead of digital timers?
Rotating bezels provide fail-safe timing that works regardless of battery life or electronic failures. The mechanical bezel can't accidentally reset or malfunction underwater, and it's instantly readable without pressing buttons or navigating menus. The unidirectional rotation prevents accidentally showing less elapsed time than actual, which could lead to dangerous extended bottom times. This simple, reliable system has proven itself over decades of use in life-or-death situations.
Q. Can automatic dive watches handle the movement and activity of diving?
Modern automatic movements in dive watches include shock protection and robust construction specifically designed for active use. The self-winding mechanism actually benefits from diving activity, as arm movements keep the mainspring wound. Quality dive watches undergo extensive testing including vibration, shock, and temperature variation trials that simulate diving conditions. Many divers prefer automatic movements for their reliability and independence from battery changes.
Q. What's the difference between water resistance ratings like ATM, bars, and meters?
These measurements represent equivalent pressure ratings: 1 ATM equals 1 bar equals 10 meters of static water pressure. A 10 ATM watch handles pressure equivalent to 100 meters depth, though this rating assumes static conditions. Dynamic pressure from swimming, showering, or diving can multiply effective pressure, which is why dive watches include safety margins. For actual diving, choose watches rated at least 200 meters (20 ATM) regardless of your maximum diving depth.
Q. How often do dive watches need maintenance and what does it involve?
Quality dive watches benefit from annual pressure testing to ensure seals remain intact, especially important for watches frequently used in saltwater. Between maintenance intervals, regular rinsing with fresh water after saltwater exposure and avoiding crown operation underwater helps maintain reliability. The robust construction of dive watches typically allows for extended use with minimal intervention when properly cared for.