The Psychology of Making: Why Building Something With Your Hands Matters
Creating something tangible with your hands triggers profound psychological responses that screens and digital work cannot replicate. The benefits of DIY projects extend far beyond the finished product, reaching into core aspects of mental health, cognitive function, and emotional well-being.
Modern research in DIY psychology reveals that hands-on creation activates multiple brain regions simultaneously, producing measurable improvements in mood, focus, and life satisfaction. Whether you're assembling furniture, crafting jewelry, or building a mechanical watch, the act of making engages your mind and body in uniquely beneficial ways.
Benefits of Creating & The Mental Health Connection
Stress Reduction Through Focused Action
Hands-on work demands present-moment attention. Your mind cannot wander to tomorrow's meeting or yesterday's argument when precise movements require full concentration.
The repetitive motions involved in most DIY projects create meditative states similar to formal mindfulness practices. Physical engagement with materials provides an anchor that pulls attention away from anxious thoughts.
Cortisol Levels Drop During Manual Work
Physical creation triggers neurochemical responses that counteract stress hormones. The tactile feedback from working with tools and materials sends calming signals to your nervous system.
Mental Stimulation and Cognitive Benefits
Problem-Solving Activates Multiple Brain Regions
Every DIY project presents unexpected challenges. Materials behave differently than planned, measurements shift, and techniques require adjustment.
These obstacles force adaptive thinking and creative solutions. Your brain builds new neural pathways as you troubleshoot problems in real-time.
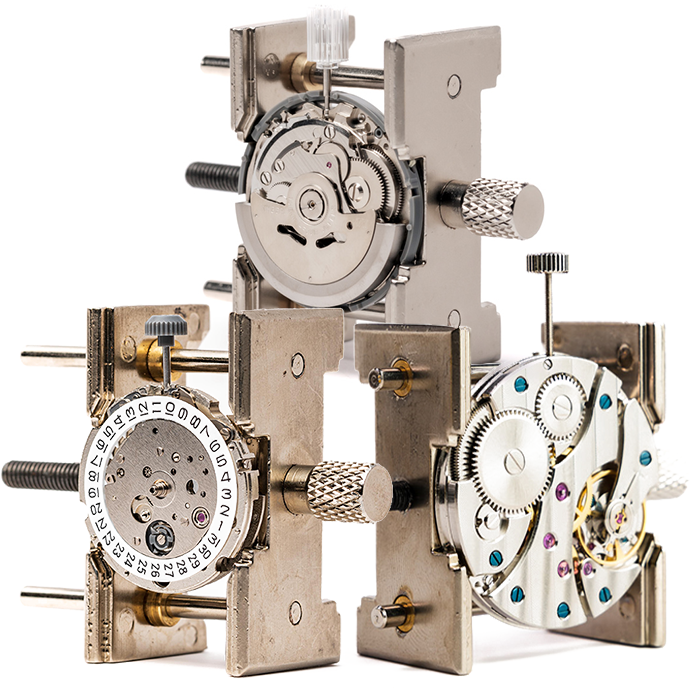
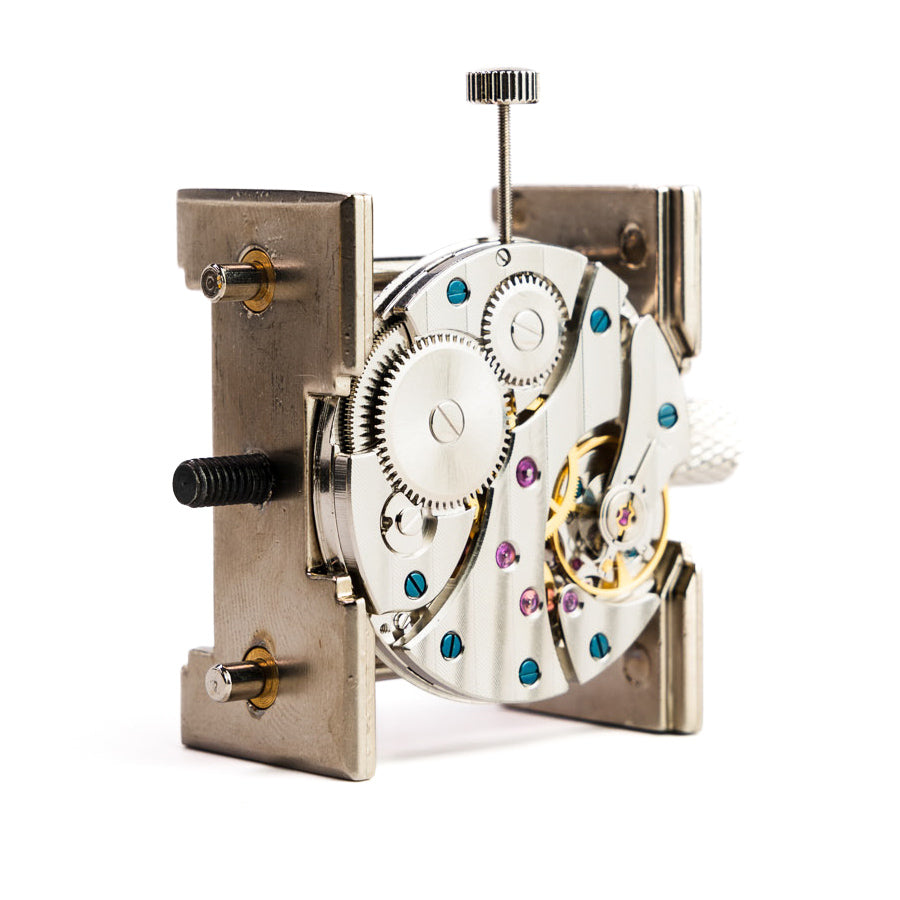
Understanding complex systems like mechanical watch movements provides particularly rich cognitive stimulation, as you must grasp how individual components interact to create precise function.
Learning New Skills Strengthens Neural Plasticity
Mastering unfamiliar techniques keeps your brain flexible and adaptive. The emotional benefits of crafting include improved memory and sustained cognitive function across age ranges.
Each new skill creates mental "scaffolding" that makes future learning easier. The confidence from previous successes carries into new challenges.
Self-Esteem and Accomplishment
Tangible Results Validate Effort
Digital work often feels ephemeral. Code can be deleted, emails disappear, and spreadsheets get updated until nothing resembles your original contribution.
Physical objects prove your capability. A completed project sits on your shelf as permanent evidence of skill and dedication.
Overcoming Difficulty Builds Confidence
The benefits of DIY projects compound when tasks challenge your current abilities. Successfully navigating difficulty teaches resilience that extends beyond the workshop.
Starting with structured approaches helps beginners build competence progressively. Beginner watchmaking guides break complex processes into manageable steps that prevent overwhelm while still providing genuine challenge.
Creative Expression and Emotional Processing
Manual Work Provides Non-Verbal Outlets
Not every emotion translates easily into words. Making things offers alternative channels for processing feelings that verbal expression cannot reach.
The emotional benefits of crafting include accessing and releasing emotions stored below conscious awareness. Hands sometimes know what minds struggle to articulate.
Personalization Creates Meaningful Objects
Adding unique touches to projects transforms functional items into personal statements. Color choices, material selections, and design modifications reflect individual taste and values.
Designing your own timepiece exemplifies this principle, allowing creators to build objects that express personal aesthetics while learning technical skills.
Mindfulness and Present-Moment Awareness
Physical Engagement Anchors Attention
Your hands provide direct connection to the present moment. The weight of tools, texture of materials, and precision of movements demand immediate awareness.
This forced presence offers respite from the constant mental chatter that characterizes modern life. DIY psychology research shows that makers report fewer intrusive thoughts during hands-on work.
Flow States Emerge Naturally
When challenge level matches skill level, consciousness shifts into "flow" where time distorts and self-consciousness disappears. This optimal experience state produces deep satisfaction and enhanced performance.
Complex assembly work, like understanding watch components, creates ideal conditions for flow experiences.
Problem-Solving and Resilience
Projects Teach Adaptive Thinking
Few things go exactly as planned. Measurements prove inaccurate, materials behave unexpectedly, and tools break mid-project.
These setbacks force creative adaptation. The resilience you develop troubleshooting practical problems strengthens your capacity to handle life's larger challenges.
Mistakes Become Learning Opportunities
Physical projects make errors immediately visible and correctable. Unlike many life situations where consequences appear slowly, DIY projects offer rapid feedback cycles that accelerate learning.
Legacy and Connection
Handmade Objects Carry Personal History
Items you build with your own hands become repositories of memory. Each scratch and imperfection recalls specific moments from the creation process.
These objects gain value beyond their material worth, especially when passed to others who recognize the effort invested.
Shared Making Strengthens Relationships
Creating alongside others builds bonds through shared struggle and mutual accomplishment. The vulnerability of learning something new together deepens trust.
Teaching skills you've mastered continues the cycle, helping others access the same benefits of creating that transformed your own experience.
Physical Well-Being
Manual Work Counters Sedentary Lifestyles
Most modern work involves minimal physical movement. Making things reintroduces varied motion that benefits overall health.
The fine motor control required for precise work maintains dexterity and hand strength across the lifespan.
Accomplishment Affects Body Chemistry
Completing projects triggers dopamine release, creating positive associations that motivate continued creative work. This natural reward system encourages beneficial habits without external pressure.
Time isn't just measured, it's built with your own hands.
Start your watchmaking journey where complete DIY kits transform curiosity into craftsmanship. Browse our collection of movement kits to find your perfect match, from complete watch kits to intricate mechanical assemblies. Your making story begins with a single component.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of DIY projects for mental health?
DIY projects reduce stress through focused attention, provide creative outlets for emotional processing, and build self-esteem through tangible accomplishments that validate your capabilities.
How does crafting improve cognitive function?
The benefits of creating include enhanced problem-solving abilities, improved neural plasticity through skill acquisition, and sustained cognitive engagement that keeps your brain active and adaptable.
Why does building things with your hands feel satisfying?
Physical creation produces tangible results that prove your competence, triggers dopamine release through accomplishment, and provides immediate feedback that creates natural flow states.
Can DIY activities help with anxiety and depression?
The emotional benefits of crafting include reduced rumination, grounding through present-moment focus, and increased self-efficacy that counters learned helplessness common in depression.
What makes hands-on work different from digital activities?
DIY psychology research shows physical engagement with materials activates different brain regions than screen-based work, providing sensory feedback and spatial reasoning that digital tasks cannot replicate.
How do I start getting the benefits of making things?
Begin with structured projects that match your current skill level, allowing you to experience accomplishment while building competence. Starting with watchmaking offers clear progression from simple to complex tasks.