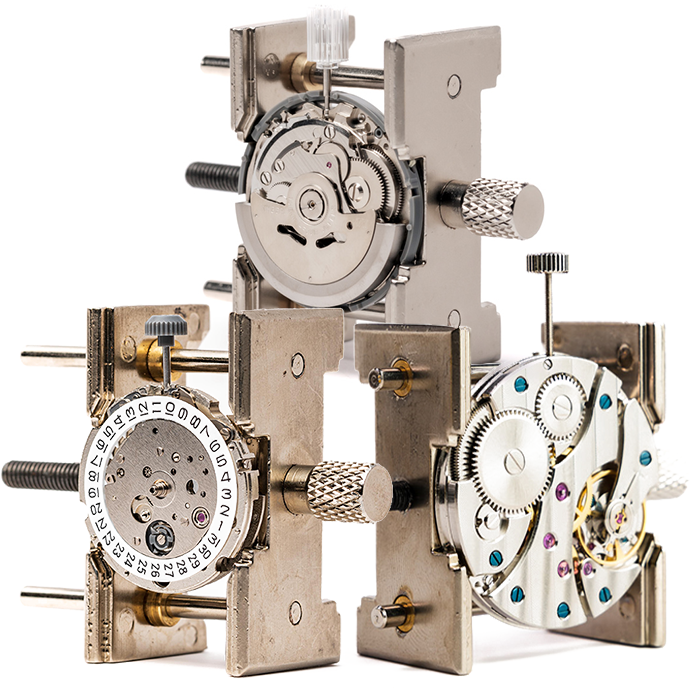
Which Movement Type Offers More Watch Complications and Features
When comparing movement types for complication capacity, mechanical watch movements reign supreme for traditional horological complications like chronographs, perpetual calendars, and minute repeaters. Quartz movements excel at feature-rich calibers with digital functions, alarms, and timers. Our complexity analysis reveals mechanical movements can accommodate 20+ complications in grand complication pieces, while quartz movements focus on practical features and accuracy. Movement comparison shows each type serves different purposes - mechanical for craftsmanship and traditional complications, quartz for precision and modern features.
The debate over which watch movement offers superior complication capacity continues to fascinate horologists and collectors alike. Understanding the fundamental differences between mechanical and quartz movements helps explain why each excels in specific areas of complexity analysis.
A watch complication refers to any function beyond displaying basic hours, minutes, and seconds. These range from simple date displays to complex astronomical indicators and chiming mechanisms.
Movement Comparison Fundamentals for Complication Capacity
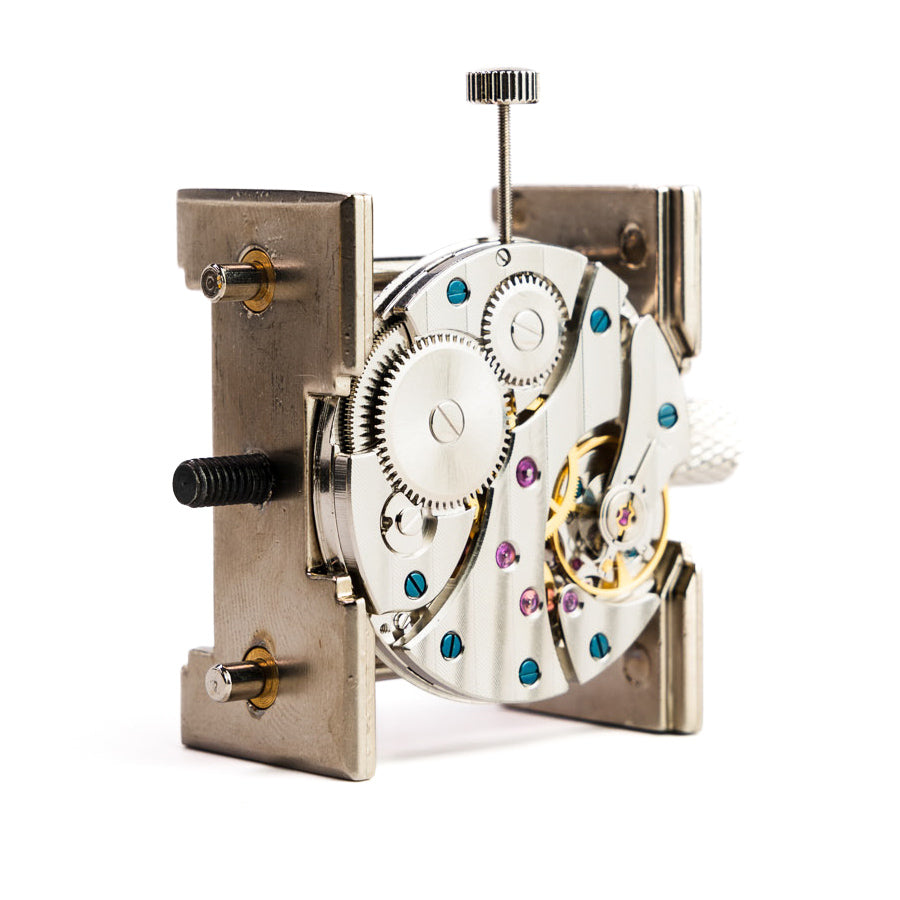
Mechanical Watch Movement Architecture and Complexity Analysis
Mechanical movements rely on intricate gear trains, springs, and levers to power complications. The energy source - a mainspring - must distribute power across multiple functions while maintaining accuracy. Feature-rich calibers like the Patek Philippe 89 demonstrate how mechanical movements can integrate dozens of complications through clever engineering.
The complexity stems from mechanical constraints. Each complication requires physical space, power allocation, and precise timing coordination. Master watchmakers spend years developing complex movements that house multiple functions without compromising reliability.
Learn more about mechanical watch fundamentals in our guide to mechanical watch basics.
Quartz Movement Design and Feature-Rich Calibers
Quartz movements use electronic circuits and stepper motors to control functions. Feature-rich calibers can incorporate multiple alarms, timers, and displays using minimal physical space. The electronic nature allows for features impossible in mechanical movements, such as precise countdown timers and multiple time zone displays.
While quartz movements excel at practical features, traditional complications like minute repeaters remain exclusive to mechanical movements due to their acoustic and mechanical nature.
Mechanical Movement Complications and Complexity Analysis
Chronograph Watch Movement Types and Variants
Chronograph movements represent one of the most popular mechanical complications. Column wheel chronographs offer superior feel and precision compared to cam-operated versions. Feature-rich calibers like the Valjoux 7750 integrate automatic winding with chronograph functions.
Flyback chronographs add instant reset capability, allowing immediate restart without stopping the chronograph first. Rattrapante (split-seconds) chronographs feature dual seconds hands for lap timing - representing the pinnacle of chronograph complexity analysis.
Calendar Movement Complications in Mechanical Watches
Calendar complications range from simple date displays to perpetual calendars that account for leap years automatically. Complex movements with annual calendars require manual correction only once yearly, while perpetual calendars theoretically run correctly until 2100.
Movement comparison shows mechanical calendar complications require extensive gear trains and programming wheels. Grande and petite sonnerie movements combine calendar functions with chiming mechanisms, creating feature-rich calibers of extraordinary complexity.
Learn about movement accuracy and complications in our mechanical watch accuracy guide.
Moon Phase and Astronomical Movement Types
Moon phase complications track lunar cycles using gear ratios calculated to match astronomical data. High-quality mechanical movements achieve accuracy within one day over 122 years. Some feature-rich calibers combine moon phases with equation of time displays and seasonal indicators.
Automatic Movement Travel Time Complications
GMT Movement Types with Independent Hour Hands
GMT complications allow tracking of two time zones simultaneously. True GMT movements feature independently adjustable hour hands, enabling quick time zone changes without stopping the watch. Movement comparison reveals that caller GMT movements (adjustable 24-hour hand) offer different functionality.
World Time Movement Complications and City Rings
World time movements display multiple time zones simultaneously using rotating city rings and 24-hour discs. These complex movements require precise gear ratios to maintain synchronization across all displayed times.
Learn more about GMT functionality in our top Swiss movements guide.
Power Reserve and Performance Movement Types
Power Reserve Movement Complications
Power reserve indicators show remaining mainspring energy in mechanical watches. Feature-rich calibers integrate these displays without compromising timekeeping accuracy. Some movements feature multiple barrels for extended power reserves exceeding 7 days.
Automatic Movement Efficiency and Rotor Systems
Automatic movements use weighted rotors to wind mainsprings through wrist motion. Efficiency varies significantly between rotor designs - micro-rotors allow thinner cases while full rotors provide superior winding. Movement comparison shows that newer automatic systems achieve 80+ hour power reserves.
Quartz Movement Types and Digital Feature-Rich Calibers
Quartz Chronograph Movement Complications
Quartz chronographs offer superior accuracy compared to mechanical versions, often measuring to 1/100th second. Feature-rich calibers combine chronograph functions with alarms, countdown timers, and lap memory. The electronic nature eliminates mechanical wear associated with repeated chronograph use.
Alarm and Timer Movement Types
Digital quartz movements excel at practical complications like multiple alarms, countdown timers, and interval timing. Complex movements can store dozens of alarms with different activation patterns. These features require minimal physical space compared to mechanical equivalents.
Learn about quartz movement fundamentals in our Japanese quartz movement guide.
Day-Date Movement Types and Display Variations
Day-date complications add weekday displays to standard date functions. Movement comparison shows that mechanical versions require additional gear trains and jumper springs, while quartz versions use simple programming. Feature-rich calibers often combine day-date functions with additional calendar information.
Movement Types Beyond Core Timekeeping
Tachymeter and External Feature-Rich Calibers
Tachymeter bezels calculate speed based on chronograph readings but don't constitute movement complications themselves. However, integrated tachymeter scales within complex movements require precise calibration and printing.
Luminous Materials and Visibility Features
Modern movement types incorporate luminous materials for low-light visibility. While not mechanical complications, these features enhance functionality. Feature-rich calibers often include multiple luminous elements for improved readability.
Tourbillon Debate in Movement Comparison
The tourbillon controversy continues among horologists. Originally designed to improve pocket watch accuracy by rotating the escapement, modern wristwatch tourbillons serve primarily aesthetic purposes. Complexity analysis shows tourbillons require significant manufacturing expertise regardless of their practical benefits.
Some consider tourbillons complications while others classify them as mechanical features. Both viewpoints have merit - tourbillons definitely increase movement complexity and manufacturing costs.
Learn about automatic watch mechanisms in our automatic watch history guide.
Final Movement Comparison Verdict
Mechanical movements offer the widest array of traditional horological complications. Complex movements can integrate 20+ functions including perpetual calendars, minute repeaters, and astronomical displays. However, manufacturing costs increase exponentially with complication count.
Quartz movements excel at practical feature-rich calibers with superior accuracy and durability. Digital functions like alarms, timers, and multiple time zones are easier to implement electronically than mechanically.
For traditional complication appreciation, mechanical movement types remain unmatched. For practical functionality and accuracy, quartz movement types offer superior value and reliability.
Consider starting your watchmaking journey with movements that match your interests - mechanical for traditional craftsmanship or quartz for modern functionality. Our Seiko NH36 Movement Kit offers hands-on experience with automatic movement construction.
Time isn't just measured, it's built with your own hands. Start your watchmaking journey with Rotate Watches, where complete DIY kits transform curiosity into craftsmanship.
Browse our collection to find your perfect match, from complete watch kits to intricate movement kits. Your watchmaking story begins with a single screw. Start building today.
FAQ
Q. Which watch movement has the most complications?
Ans. Mechanical movements hold the record for most complications, with pieces like the Patek Philippe Grandmaster Chime featuring 20 complications including minute repeater, perpetual calendar, and astronomical displays.
Q. Can quartz movements have complications like perpetual calendars?
Ans. Yes, some high-end quartz movements feature perpetual calendars using electronic programming. Citizen's Campanola series includes quartz perpetual calendars that remain accurate until 2100.
Q. Is automatic different from mechanical movement?
Ans. Automatic movements are a subset of mechanical movements featuring self-winding rotors. All automatic movements are mechanical, but not all mechanical movements are automatic - some require manual winding.
Q. What is a watch complication?
Ans. A watch complication is any function beyond displaying basic hours, minutes, and seconds. Examples include chronographs, calendars, moon phases, and GMT displays.
Q. Is a tourbillon considered a watch complication?
Ans. The tourbillon's classification remains debated. Some consider it a complication due to manufacturing complexity, while others classify it as a mechanical feature since it primarily affects visual appeal rather than adding functionality.
Q. Which movement type offers better accuracy for complications?
Ans. Quartz movements provide superior accuracy for timekeeping functions and complications. Mechanical movements offer traditional craftsmanship and intricate complication integration but with less precision than electronic counterparts.
{ "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "FAQPage", "mainEntity": [ { "@type": "Question", "name": "Which watch movement has the most complications?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Mechanical movements hold the record for most complications, with pieces like the Patek Philippe Grandmaster Chime featuring 20 complications including minute repeater, perpetual calendar, and astronomical displays." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Can quartz movements have complications like perpetual calendars?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Yes, some high-end quartz movements feature perpetual calendars using electronic programming. Citizen's Campanola series includes quartz perpetual calendars that remain accurate until 2100." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Is automatic different from mechanical movement?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Automatic movements are a subset of mechanical movements featuring self-winding rotors. All automatic movements are mechanical, but not all mechanical movements are automatic - some require manual winding." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "What is a watch complication?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "A watch complication is any function beyond displaying basic hours, minutes, and seconds. Examples include chronographs, calendars, moon phases, and GMT displays." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Is a tourbillon considered a watch complication?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "The tourbillon's classification remains debated. Some consider it a complication due to manufacturing complexity, while others classify it as a mechanical feature since it primarily affects visual appeal rather than adding functionality." } }, { "@type": "Question", "name": "Which movement type offers better accuracy for complications?", "acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Quartz movements provide superior accuracy for timekeeping functions and complications. Mechanical movements offer traditional craftsmanship and intricate complication integration but with less precision than electronic counterparts." } } ] }