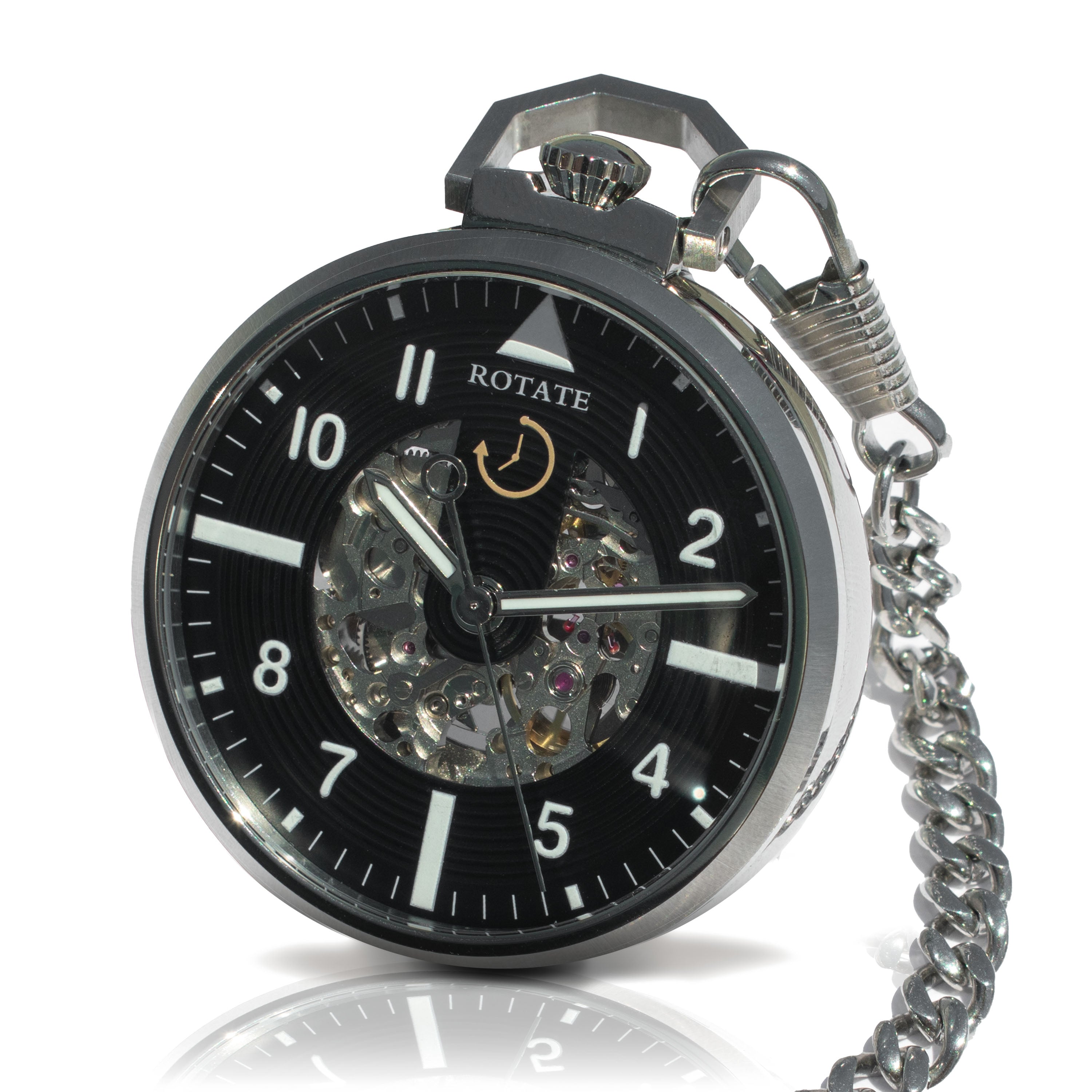
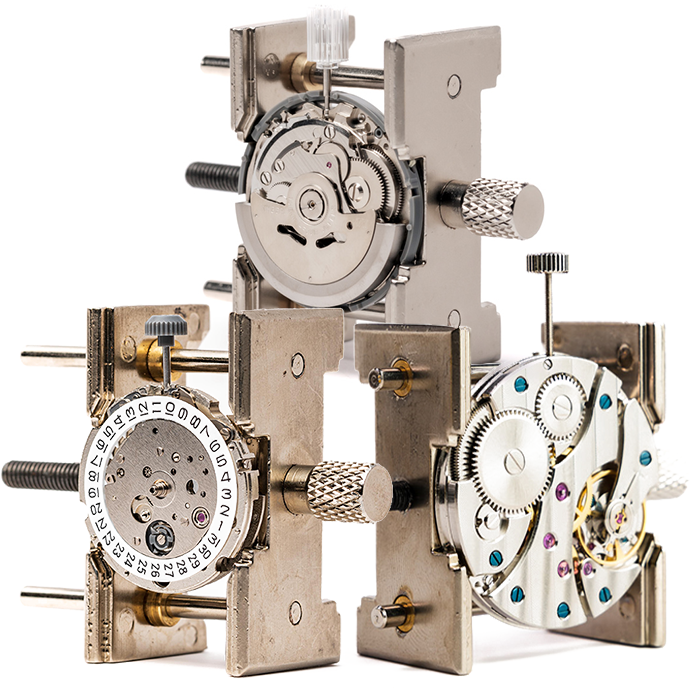
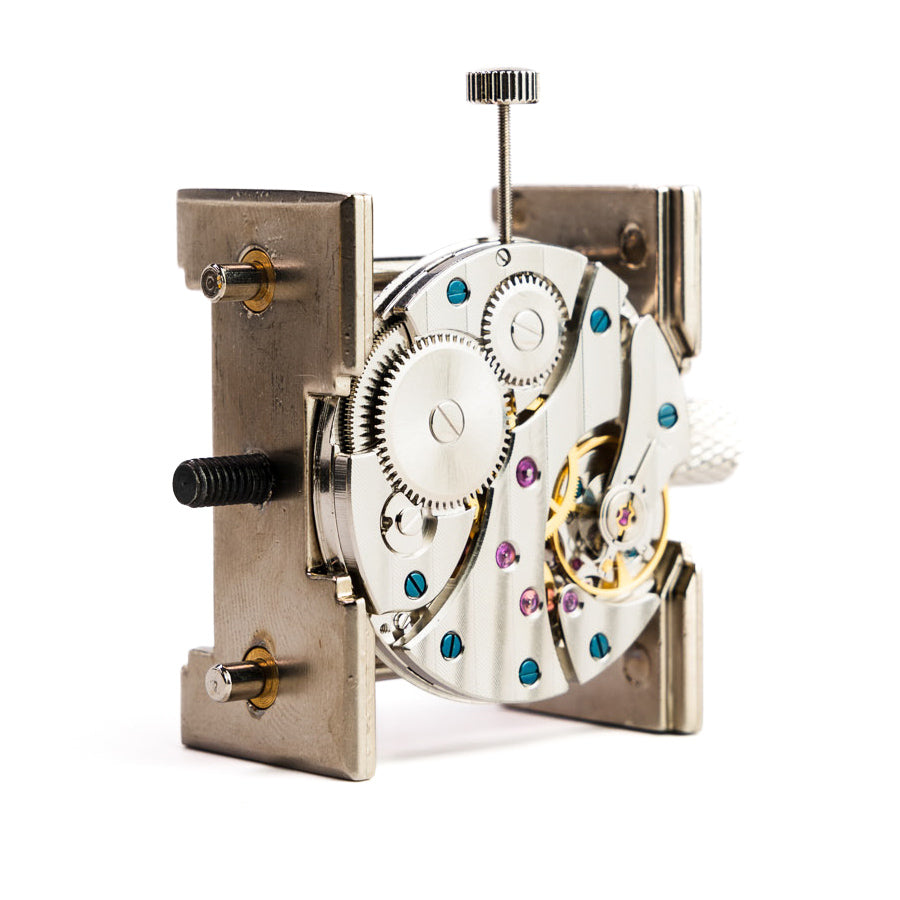
How Does the Miyota 8N24 Movement Work?
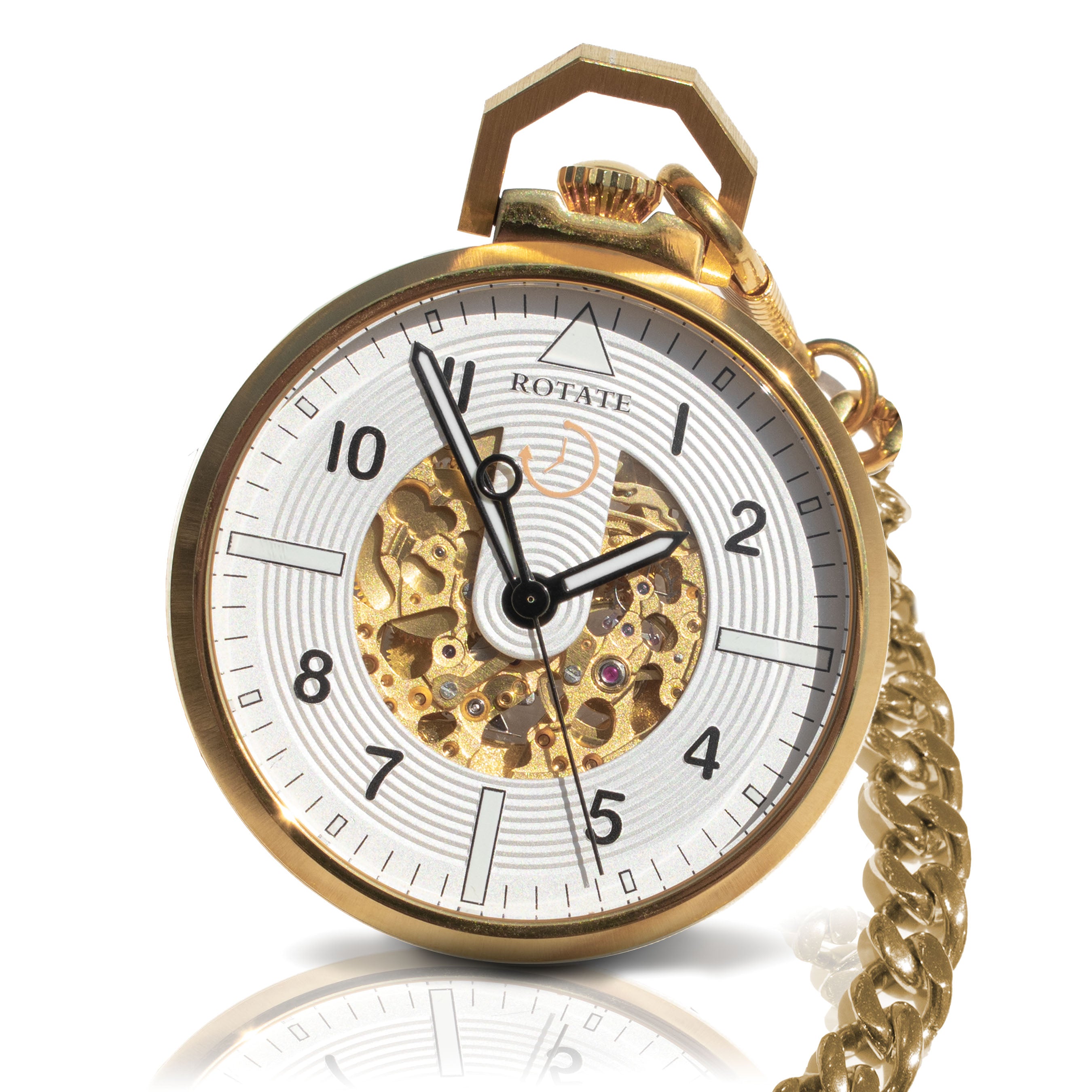
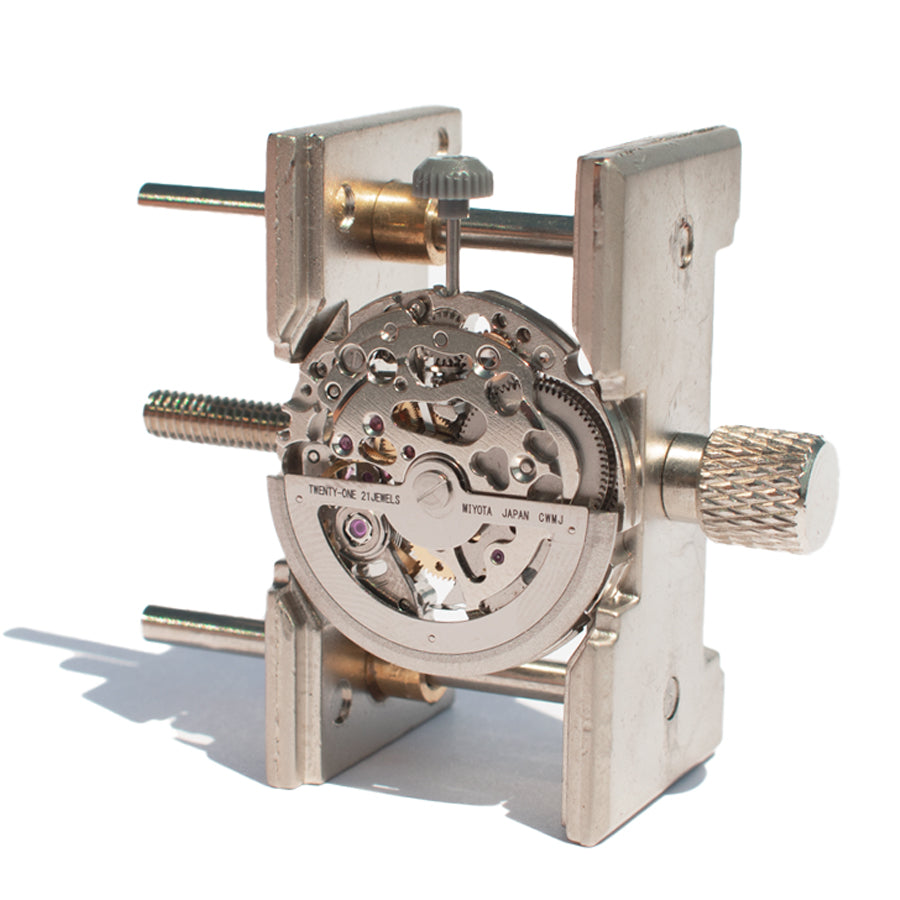
The Miyota 8N24 reveals its inner workings through skeleton design. You see gears turning, balance wheels oscillating, and mechanisms operating. Watching parts move teaches how automatic movements function.
Understanding skeleton movements reveals mechanical principles invisible in traditional solid movements. The 8N24 belongs to Miyota's Cal. 82 series, first introduced in 1975 and supplied worldwide for nearly 40 years.
Cal. 8N24 Development and History
Miyota introduced the Cal. 8N24 in 2006 as part of their standard automatic movement lineup. The caliber builds on the proven Cal. 82 series architecture refined over decades.
The Cal. 82 series became the most widespread mechanical movement globally. Miyota supplies these movements to watch brands worldwide. Main plates and components are manufactured in Japanese factories using automated assembly lines.
Mass Production Excellence
Miyota achieves mechanical movement mass production through techniques developed for analog quartz manufacturing. Few Japanese companies can manufacture mechanical movements at this scale.
Automated assembly lines at the Iida Factory use precision parts processing and proprietary assembly devices. Full automation becomes possible through exact parts tolerances and specialized equipment.
Movement Specifications
The 8N24 measures standard automatic movement dimensions suitable for various watch cases. Skeleton architecture removes unnecessary material while maintaining structural integrity.
Key specifications include:
- Automatic winding with manual capability
- Standard mechanical accuracy
- Approximately 42 hours power reserve
- 21,600 vibrations per hour (indirect seconds)
- Available in silver and gold finishes
Automatic Winding Mechanism
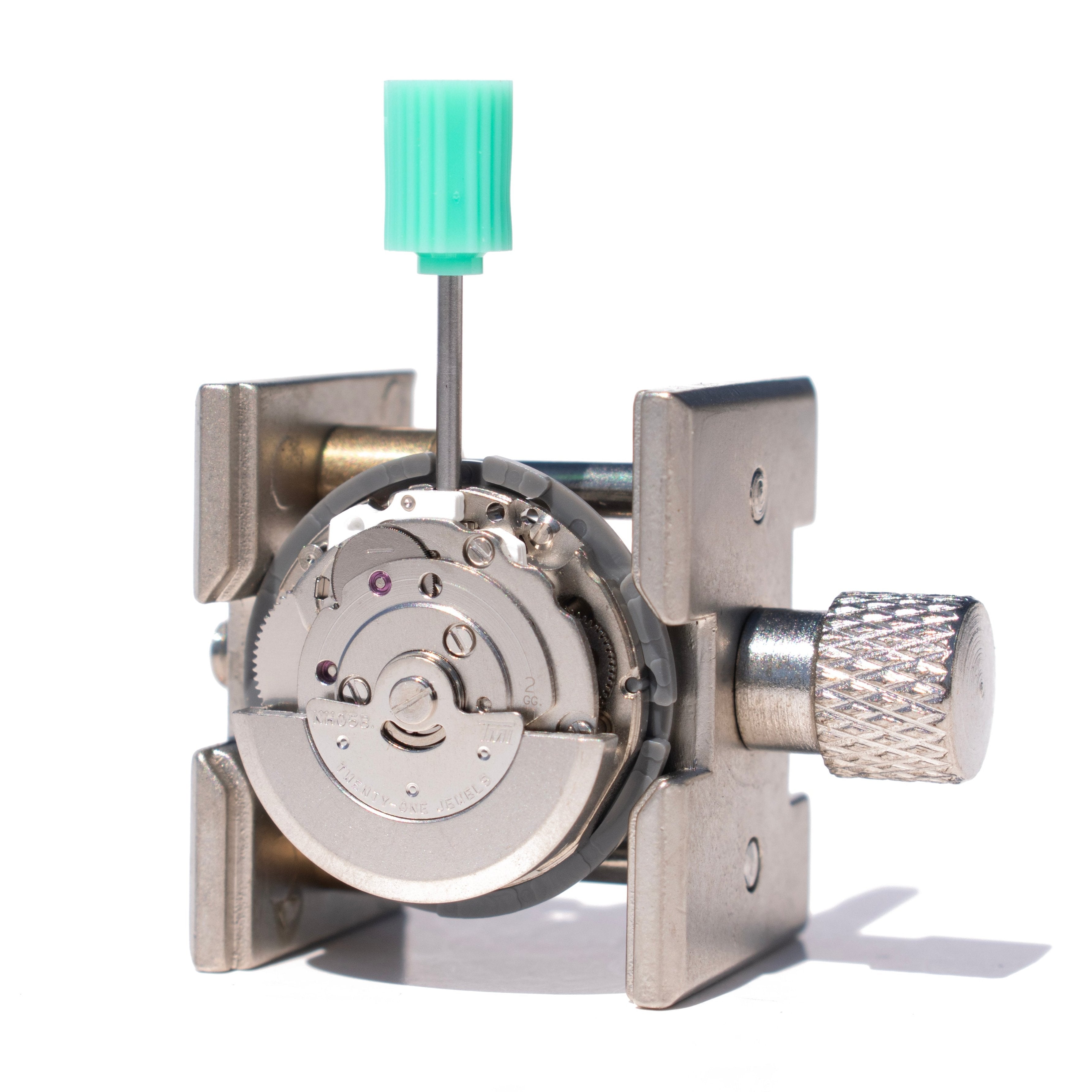
The movement uses automatic rotor spinning through wrist motion. Rotation winds the mainspring storing mechanical energy for timekeeping.
Visible Rotor Operation
Skeleton design lets you watch automatic winding happen. Move your wrist and see the rotor respond immediately. The weighted rotor continues spinning from inertia when motion stops.
Energy transfers through reduction gears to the mainspring barrel. Pawl mechanisms allow winding rotation while preventing reverse unwinding.
Power Flow Through Gear Train
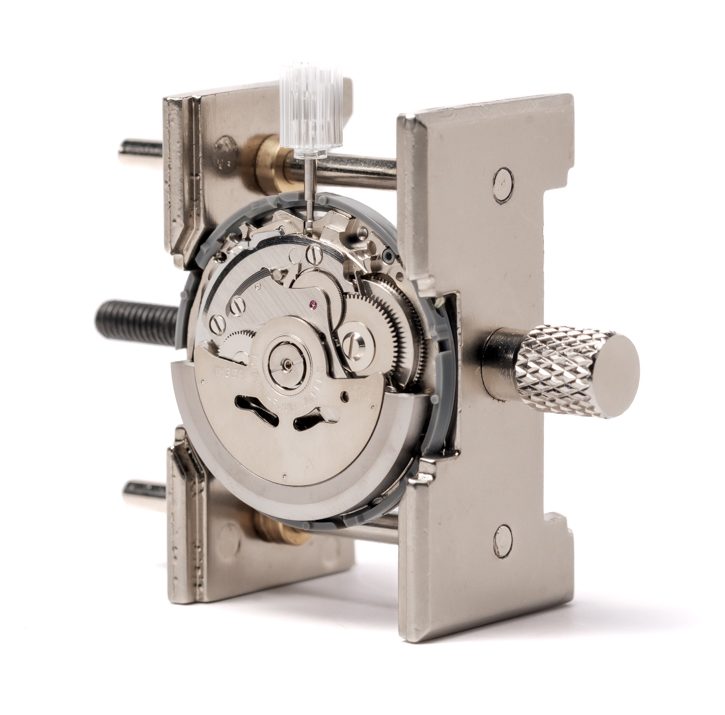
Wound mainspring slowly releases stored energy. The gear train transmits power from the barrel through multiple stages to escapement.
Train Wheel Architecture
Beautiful train wheels showcase in skeleton designs. The movement works well for rear skeleton watches or open heart designs showing balance wheel movement.
The center wheel rotates once per hour, driving a minute hand. The third wheel transmits power to the fourth wheel. The fourth wheel drives seconds hand through indirect seconds configuration.
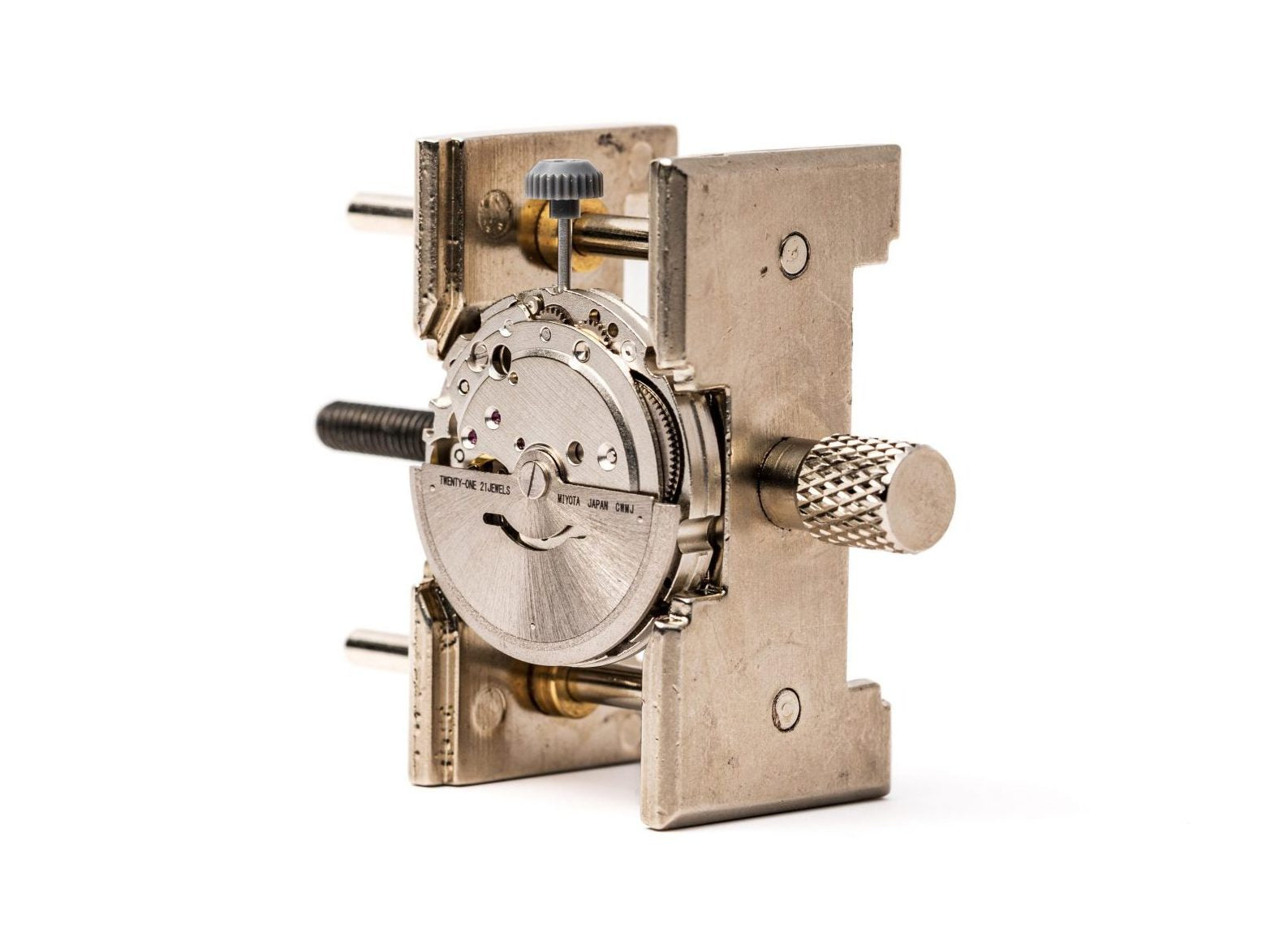
Escapement and Balance Assembly
The escapement controls energy release creating characteristic ticking. Pallet fork and escape wheel work together regulating timekeeping.
Balance Wheel Construction
Balance wheels in Miyota movements receive human hand assembly despite some automation. Adjusting eccentricity and horizontality of balance spring requires technique that cannot be expressed numerically.
Skilled technicians handle the most delicate procedures. The balance represents the heart of the watch, key to accuracy.
Jeweled Pallet Fork
The jeweled pallet fork and staff measure grain-of-rice size yet contain five parts. Precision assembly of tiny components demonstrates manufacturing expertise.
Assembly Line Process
Miyota assembles movements using automated lines incorporating decades of mass production expertise. Precision parts processing enables high-precision automated assembly.
Quality Control Steps
Multiple inspection stages check:
- Component height and alignment
- Screw tightening torque
- Missing parts detection
- Damage identification
Computerized exterior checks analyze digital photos detecting flaws. Specialized computers identify missing parts or major damage. Defective parts are automatically removed from assembly lines.
Worker Inspection
Workers use microscopes inspecting parts at intermediate assembly stages. Human verification supplements automated checking.
Balance wheel insertion, normally a nerve-wracking manual process, occurs through automation. Careful part checking ensures quality.
Skeleton Design Applications
Open architecture creates visually interesting watches. Skeleton movements work particularly well for:
- Rear skeleton case backs
- Open heart dials (showing balance at 7 o'clock)
- Full skeleton watches revealing entire mechanism
Mechanical movement enthusiasts appreciate seeing inner workings. Visual interest adds appeal beyond pure timekeeping function.
Using 8N24 in Watch Projects
Building skeleton watches creates striking finished pieces. Dial-less or partially open dials showcase movement best.
Installation follows standard automatic movement procedures. Case compatibility and proper assembly ensure reliable operation.
Aesthetic Considerations
Choose dials and case backs revealing movement architecture. Open designs defeat skeleton movement purpose if components remain hidden.
Finished watches create conversation pieces. Visible gears and operating balance wheels fascinate people unfamiliar with mechanical movements.
Conclusion
The Miyota 8N24 transforms mechanical watches from sealed mysteries into visible operating machines. Skeleton architecture demonstrates engineering principles through functioning examples.
Cal. 82 series reliability combines with visual interest creating appealing movements for watch enthusiasts. Mass production expertise ensures consistent quality and worldwide availability.
Rotate Watches offers watch kits featuring visible mechanical operation. Quality components and detailed guides help you build timepieces showcasing movement architecture.
Create functioning mechanical art through hands-on building. Start your skeleton watch project today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you service skeleton movements yourself?
Skeleton movements service like traditional movements. Visible architecture helps identify problems. Complete disassembly requires skills developed through practice and proper tools.
Do skeleton movements keep accurate time?
Accuracy depends on manufacturing quality and regulation, not skeleton design. Properly regulated skeleton movements perform identically to traditional sealed movements.
Are skeleton movements more fragile?
Reduced material in bridges requires careful design and maintaining strength. Quality skeleton movements achieve adequate durability for normal wear.
Why don't all movements use skeleton designs?
Skeletonization adds manufacturing cost. Many prefer traditional solid movements and decorative dials. Skeleton remains a specialty aesthetic choice.
Can you see the mainspring in 8N24?
The mainspring sits inside barrel housing. Complete mainspring visibility is less common. Barrel design typically keeps springs protected.
Does skeleton design need special maintenance?
No special maintenance required. Service intervals and procedures match traditional movements. Visibility actually helps monitor movement conditions.